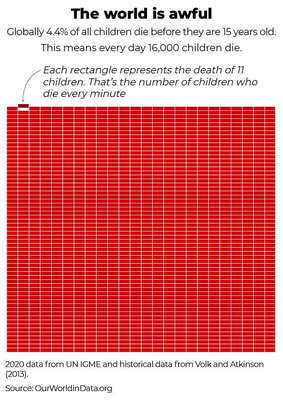
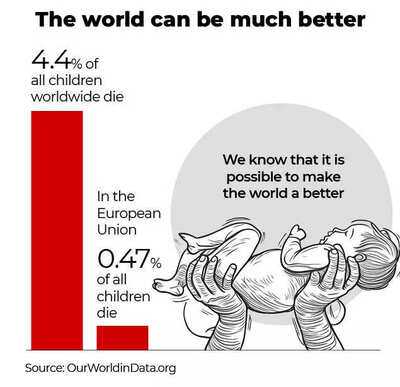
A visualization from Our World in Data (OWID), drawing on 2020 estimates from the UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation, shows the world’s stark child-mortality paradox . Globally, 4.4% of all children die before age 15 - roughly 16,000 deaths every day. Historically, the rate was far worse: around half of all children died in many parts of the world in earlier centuries. Today’s global average masks a wide range: in the European Union it’s about 0.47%, showing what’s achievable with strong health systems and broad prosperity.

Why it matters
Child mortality is the most basic test of whether societies protect the vulnerable. Each percentage point represents hundreds of thousands of young lives and the futures of families and communities.
Progress, in perspective
Vaccines, antibiotics, safer childbirth, clean water and sanitation, and better nutrition have driven a historic collapse in child deaths over the last century. That “much better” story matters: it proves that policy, science and investment work when they reach people at scale.
The gap to close
The EU’s 0.47% rate demonstrates that 4.4% is not inevitable. The burden remains concentrated in the poorest regions, where conflict, weak health systems and preventable diseases (pneumonia, diarrhea, and malaria) still kill many children. Proven interventions - full immunization, mosquito-net coverage, oral rehydration therapy, fortified foods, and access to primary care - are affordable compared with the human and economic costs of inaction.
What’s next
Sustaining gains means protecting routine immunization, strengthening community health workers, and targeting “last-mile” access in fragile settings. The lesson from OWID’s chart is clear: the world is awful and much better at the same time - and it can be much better still.

Why it matters
Child mortality is the most basic test of whether societies protect the vulnerable. Each percentage point represents hundreds of thousands of young lives and the futures of families and communities.
Progress, in perspective
Vaccines, antibiotics, safer childbirth, clean water and sanitation, and better nutrition have driven a historic collapse in child deaths over the last century. That “much better” story matters: it proves that policy, science and investment work when they reach people at scale.
The gap to close
The EU’s 0.47% rate demonstrates that 4.4% is not inevitable. The burden remains concentrated in the poorest regions, where conflict, weak health systems and preventable diseases (pneumonia, diarrhea, and malaria) still kill many children. Proven interventions - full immunization, mosquito-net coverage, oral rehydration therapy, fortified foods, and access to primary care - are affordable compared with the human and economic costs of inaction.
What’s next
Sustaining gains means protecting routine immunization, strengthening community health workers, and targeting “last-mile” access in fragile settings. The lesson from OWID’s chart is clear: the world is awful and much better at the same time - and it can be much better still.
You may also like

India's industrial production clocks 4 per cent growth in September

MP: Bulls trigger boiling oil horror at Bageshwar Dham; toddler burned, vendor injured

Find out which Aadhaar center is closest to you from the comfort of your home.

Signs of Heart Disease: The body starts giving signals a few hours before a heart attack; if understood, then life can be saved.

Odisha CM reiterates 'Zero Casualty' target as state braces for Cyclone Montha






